The Bowtie Methodology is a powerful tool not only for risk management but also for auditing processes. Its visual representation of barriers and controls makes it an effective way to identify gaps and ensure compliance with safety systems. Here’s how you can use Bowtie for auditing purposes:
1. Align the Bowtie Diagram with Audit Objectives
- Step 1: Define the purpose of the audit (e.g., regulatory compliance, system effectiveness, or gap analysis).
- Step 2: Ensure the Bowtie diagram reflects the specific hazards, threats, and consequences relevant to the audit scope.
- Outcome: A targeted framework for evaluating the effectiveness of barriers.
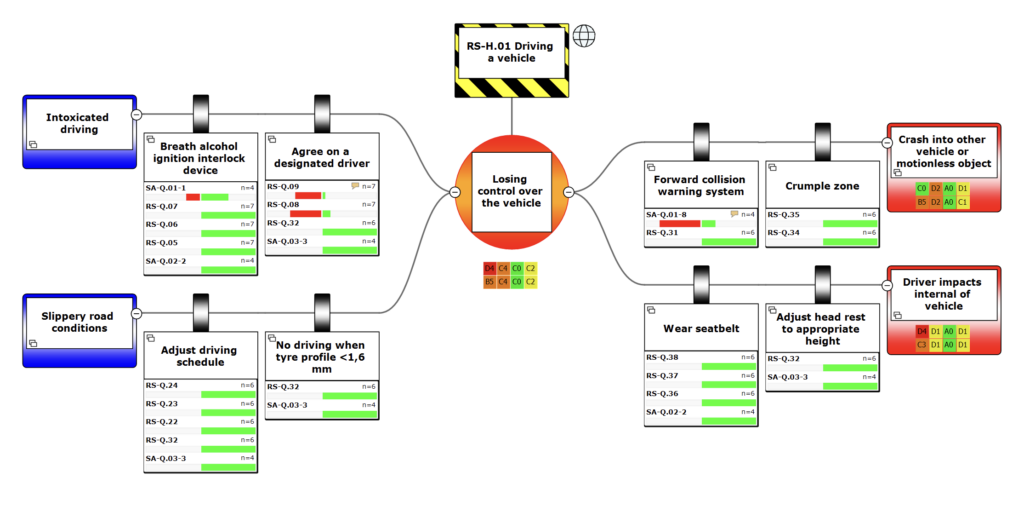
2. Assess Barrier Effectiveness
- Use the Bowtie diagram to systematically review all preventive and mitigative barriers:
- Preventive Barriers: Controls designed to stop threats from causing incidents.
- Mitigative Barriers: Controls to minimize the impact if an incident occurs.
- Audit Questions:
- Are the barriers well-maintained and functioning as intended?
- Are responsibilities for maintaining barriers clearly assigned?
- Have any barriers failed or been bypassed?
- Documentation: Note deficiencies in barrier performance or maintenance.
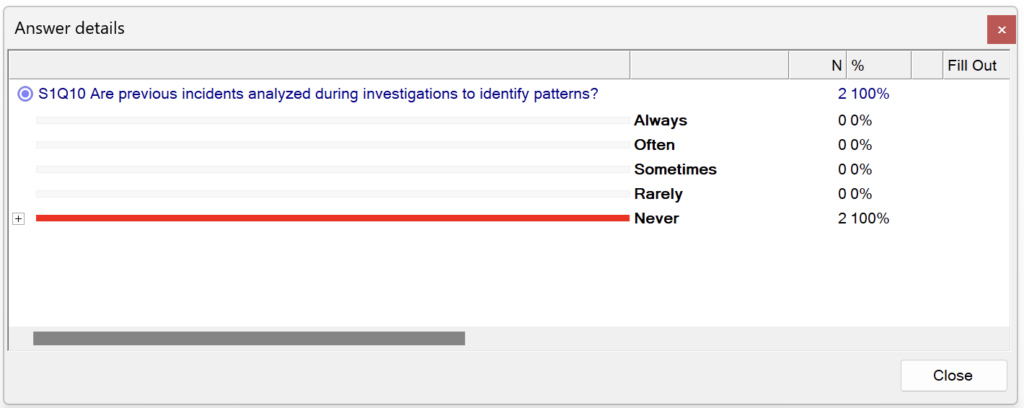
3. Verify the Completeness of Barriers
- Cross-check the Bowtie diagram against:
- Organizational policies and procedures.
- Regulatory and industry standards.
- Identify missing or incomplete barriers that could lead to system vulnerabilities.
4. Use Bowtie for Compliance Auditing
- Map Bowtie barriers to compliance requirements (e.g., OSHA, ISO 45001).
- During the audit, check if the controls meet the regulatory standards and are adequately documented.
- Highlight non-conformities for corrective actions.
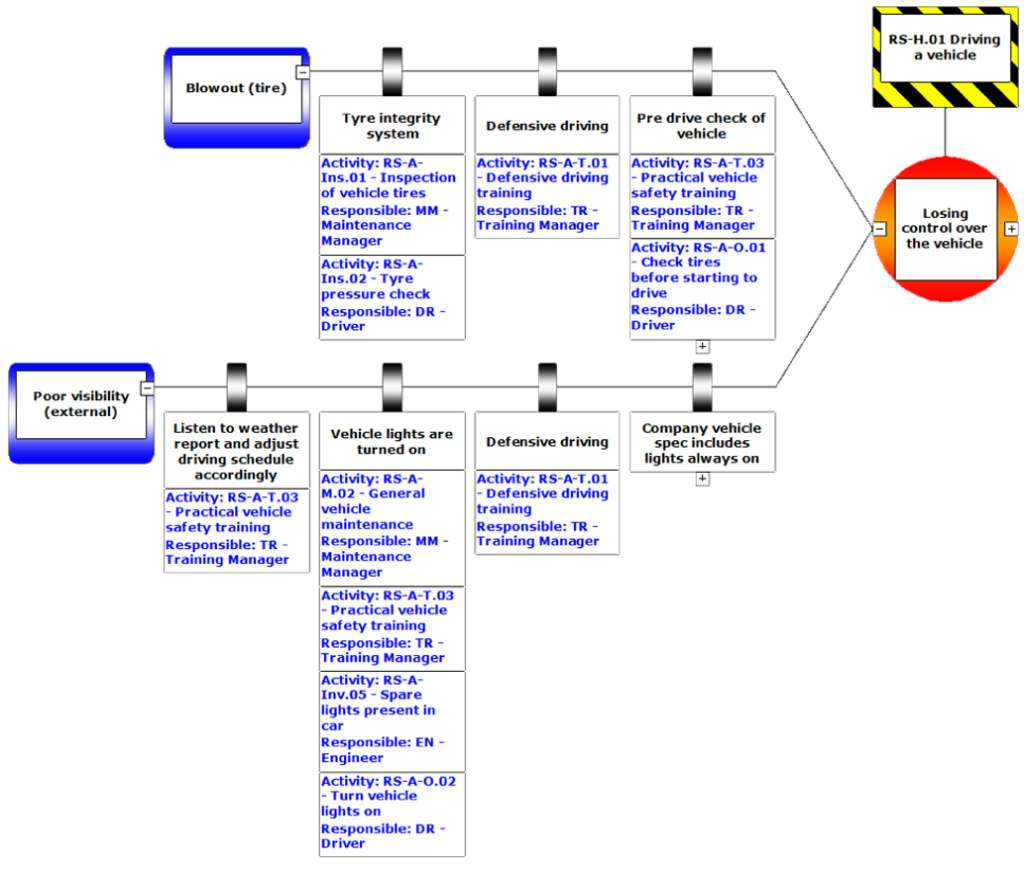
5. Integrate Human Factors into the Audit
- Use the Bowtie diagram to examine:
- Human Reliability: Are workers trained to operate and maintain barriers effectively?
- Management Systems: Are supervision and safety culture supporting barrier effectiveness?
6. Audit Incident Preparedness and Response
- Review mitigative barriers to ensure the organization is prepared for potential consequences.
- Check if emergency plans, communication systems, and recovery measures are aligned with the Bowtie diagram.
7. Identify Opportunities for Improvement
- Use findings from the audit to update the Bowtie diagram:
- Add new barriers where gaps are identified.
- Strengthen weak barriers with additional measures.
- Eliminate redundant or ineffective barriers.
8. Communicate Audit Results with Bowtie
- Present audit findings using the Bowtie diagram to provide:
- A clear, visual overview of current risks and barrier performance.
- Actionable insights for stakeholders to prioritize improvements.
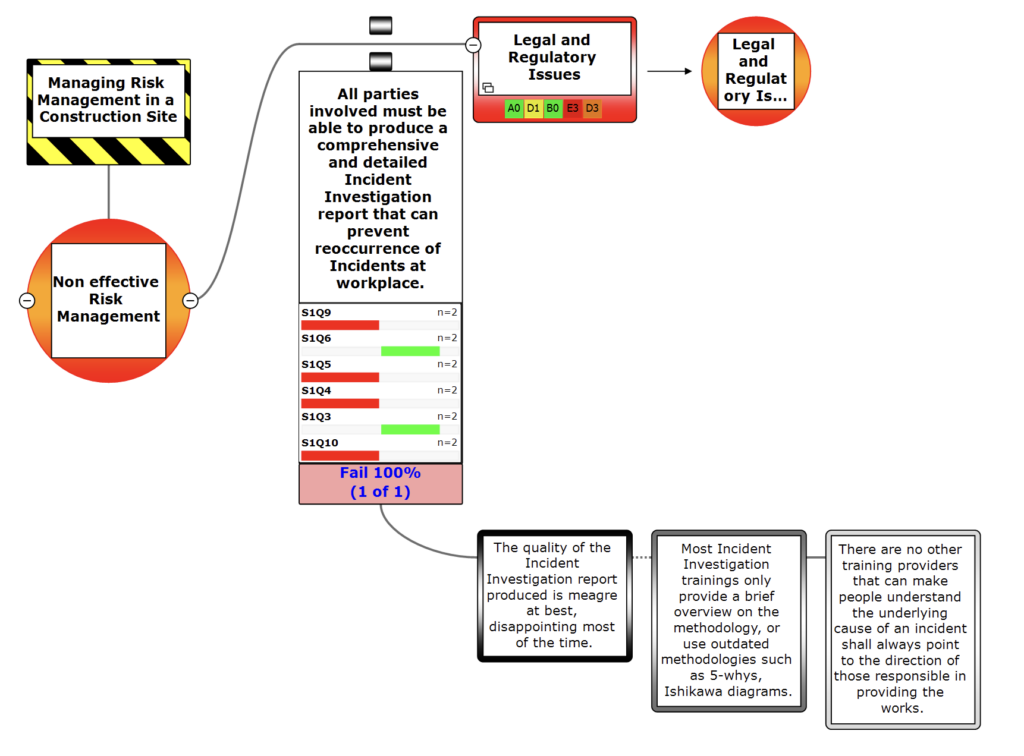
Example: Auditing with Bowtie
Scenario:
Auditing a refinery’s risk management system for fire hazards.
- Threats: Equipment malfunction, human error, or external ignition sources.
- Preventive Barriers: Regular equipment maintenance, operator training, automated shutdown systems.
- Mitigative Barriers: Fire suppression systems, evacuation plans, emergency response teams.
Audit Steps:
- Verify the functionality of automated shutdown systems.
- Check maintenance logs for firefighting equipment.
- Ensure all employees are trained in emergency evacuation procedures.
Benefits of Using Bowtie for Auditing
- Clarity: Provides a visual representation of system performance.
- Focus: Targets key risk areas and barriers for detailed review.
- Actionability: Converts audit findings into concrete improvement actions.
Conclusion
Using Bowtie for auditing ensures a structured and barrier-focused approach, helping organizations maintain compliance and enhance safety performance. By systematically assessing barriers, identifying gaps, and updating the Bowtie diagram, you can create a continuous improvement loop for your risk management system.
