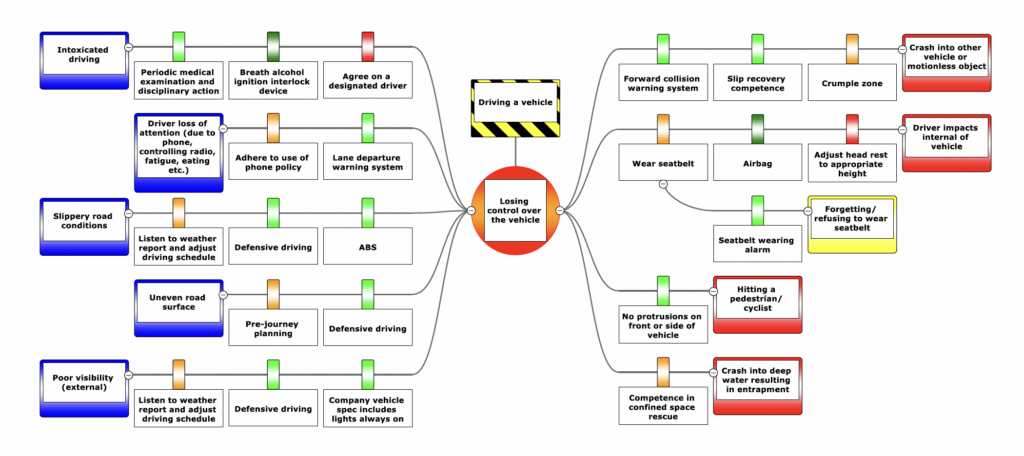
The Bowtie Methodology is a risk management tool that provides a clear, visual way to identify and manage hazards, threats, and their consequences. Named for its resemblance to a bowtie, this diagramming method helps organizations proactively analyze risks and design effective barriers to prevent accidents or minimize their impact.
Key Components of the Bowtie Diagram
- Hazard (The Knot of the Bowtie):
- The central focus of the diagram, representing a potential source of harm.
- Example: “Handling flammable chemicals.”
- Threats (Left Side):
- Events or conditions that could trigger the hazard.
- Example: “Spillage during transfer.”
- Consequences (Right Side):
- Potential outcomes if the hazard is not controlled.
- Example: “Fire causing injury or property damage.”
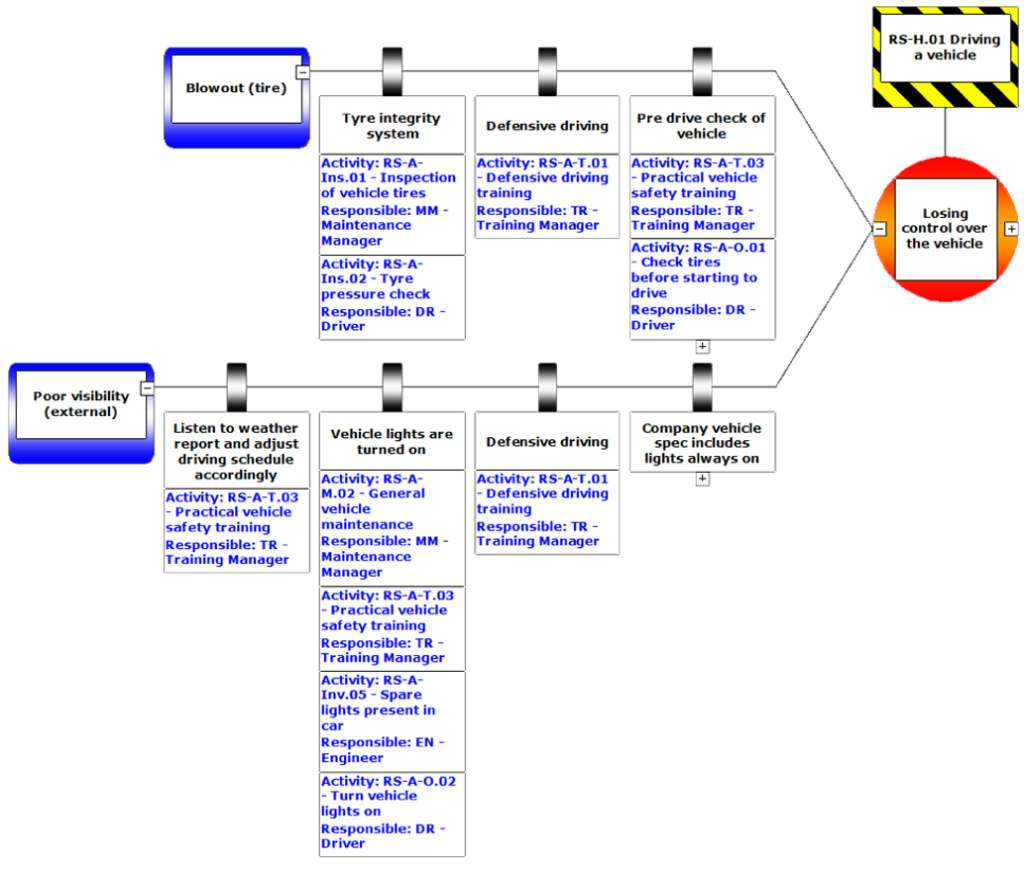
- Preventive Barriers (Left Side, Before the Hazard):
- Measures that reduce the likelihood of the threat leading to the hazard.
- Example: “Secondary containment systems.”
- Mitigative Barriers (Right Side, After the Hazard):
- Measures that reduce the severity of consequences if the hazard materializes.
- Example: “Fire suppression systems.”
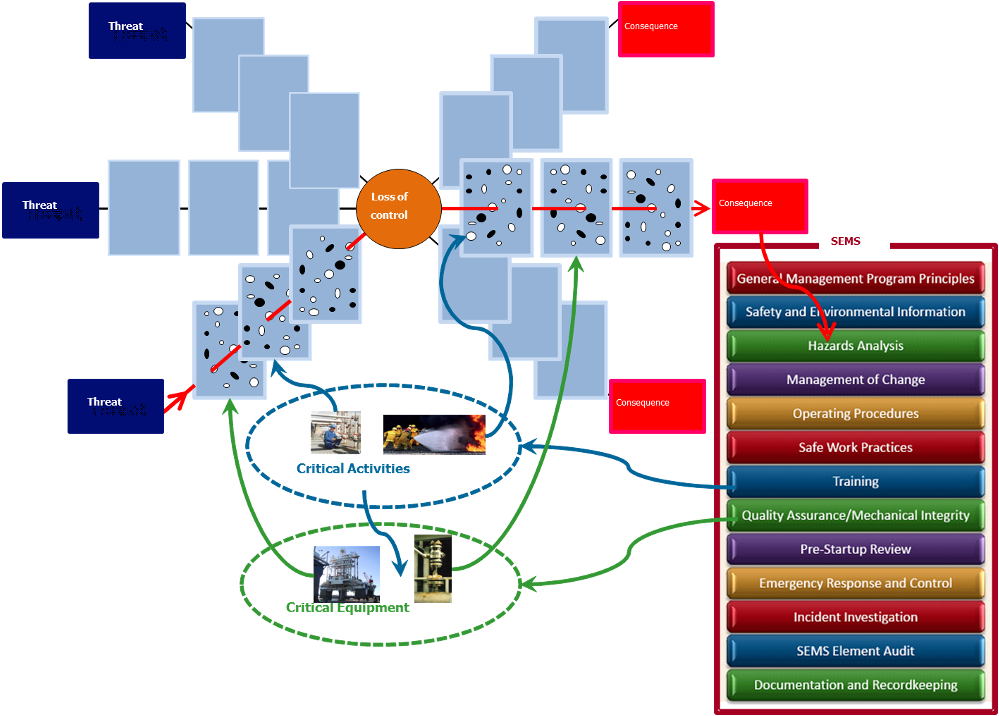
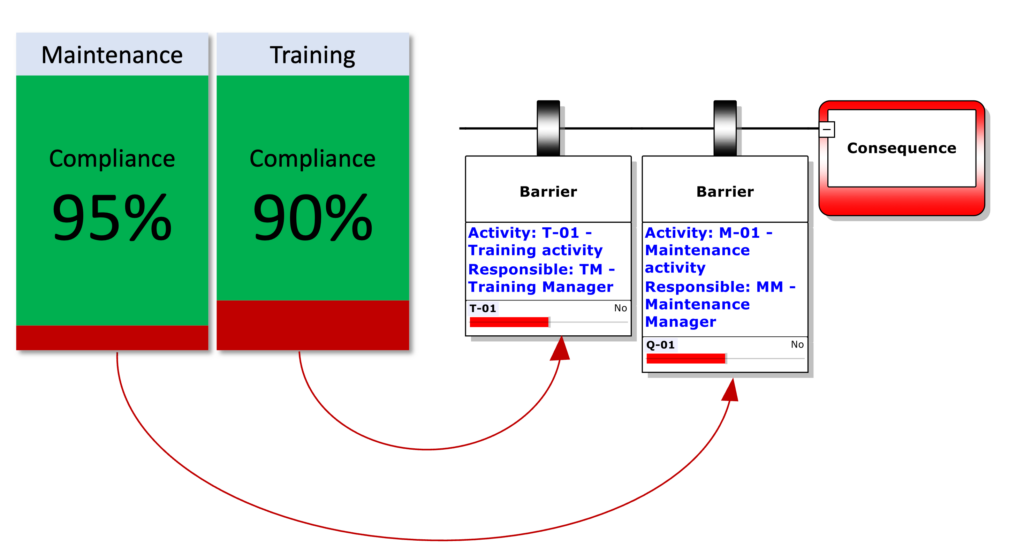
- Escalation Factors and Controls:
- Conditions that could weaken barriers and the controls in place to counteract them.
- Example: “Equipment wear and tear” with “regular maintenance” as a control.
How the Bowtie Works
The diagram’s left side focuses on prevention, detailing what must be done to stop threats from escalating into hazardous events. The right side emphasizes mitigation, outlining steps to minimize harm if the hazard occurs.
This dual approach ensures that both proactive (preventive) and reactive (mitigative) measures are in place, creating a comprehensive risk management strategy.
Advantages of the Bowtie Method
- Simplicity and Clarity:
- Converts complex risk scenarios into an easy-to-understand visual format.
- Holistic View of Risks:
- Shows how threats, hazards, and consequences are interrelated.
- Barrier Management:
- Highlights the role of barriers and the importance of maintaining them.
- Proactive Risk Management:
- Helps organizations identify gaps in safety systems before incidents occur.
- Communication Tool:
- Ideal for engaging stakeholders, from front-line workers to management.
When to Use the Bowtie Method
- High-Risk Activities: Industries like oil and gas, aviation, or chemical processing often use Bowtie diagrams to manage risks.
- Safety Case Development: To meet regulatory requirements or safety audits.
- Operational Risk Assessments: During project planning, maintenance, or hazard reviews.
Examples of Bowtie in Action
- Oil and Gas Industry: Managing risks associated with offshore drilling operations.
- Healthcare: Preventing medical errors in surgical procedures.
- Construction: Managing risks of working at heights or heavy machinery.
How Bowtie Complements Other Tools
The Bowtie method is proactive, but it can be linked with reactive tools like Tripod Beta for a continuous risk management cycle:
- Use Bowtie to design barriers.
- Investigate incidents with Tripod Beta when barriers fail.
- Update the Bowtie diagram based on lessons learned.
Conclusion
The Bowtie methodology is a powerful tool for proactive risk management, offering a visual framework to identify, assess, and control risks. By focusing on barriers, it ensures organizations can prevent incidents or minimize their impact, fostering a culture of safety and accountability.
