Both Bowtie and Tripod Beta are barrier-based methodologies that help manage risks and prevent incidents, but they serve different purposes in the risk management process. While Bowtie takes a proactive approach to managing risks, Tripod Beta is reactive, focusing on investigating incidents. Here’s a breakdown of their differences and how they can complement each other.
1. Purpose and Approach
Bowtie Method
- Purpose: Proactively identify and manage risks before incidents occur.
- Approach:
- Visualizes potential hazards, threats, and consequences in a clear diagram.
- Focuses on identifying and strengthening barriers that prevent incidents or mitigate consequences.
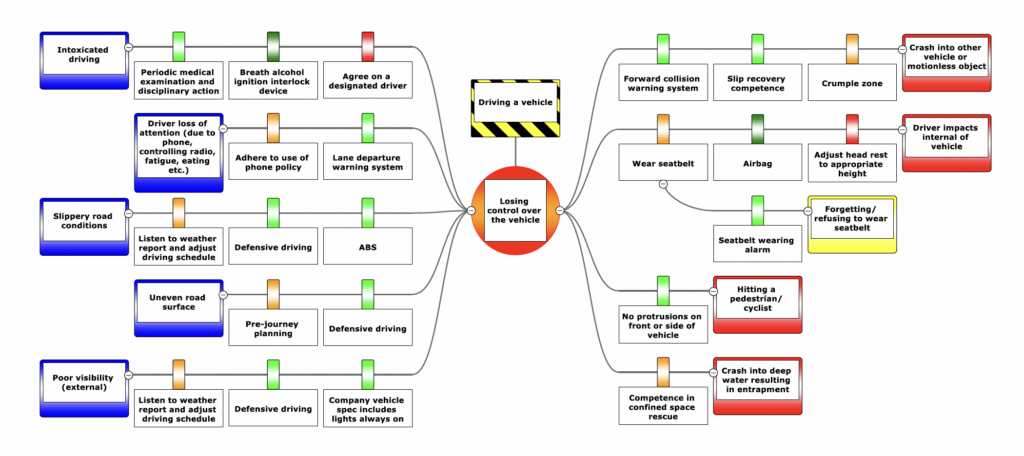
Tripod Beta
- Purpose: Reactively investigate incidents to uncover root causes and systemic failures.
- Approach:
- Analyzes what went wrong and why it happened after an incident occurs.
- Identifies barriers that failed or were absent and addresses underlying systemic issues.

2. Timing of Application
- Bowtie: Used during risk assessment and planning stages. Ideal for high-risk processes or activities to preemptively address potential threats.
- Tripod Beta: Applied after an incident to investigate and prevent recurrence by identifying root causes and systemic weaknesses.
3. Focus Areas
Bowtie Method
- Emphasizes hazard identification and barrier management.
- Focuses on both preventive barriers (to stop an incident from occurring) and mitigative barriers (to reduce the severity of consequences).
Tripod Beta
- Emphasizes incident investigation and root cause analysis.
- Focuses on latent conditions (systemic issues), active failures, and barrier weaknesses that contributed to the incident.
4. How They Are Interlinked
Bowtie and Tripod Beta can complement each other, forming a closed-loop system for continuous improvement:
- Proactive with Bowtie:
- Use Bowtie to identify potential hazards and design effective barriers.
- Regularly monitor and maintain barriers to ensure their effectiveness.
- Reactive with Tripod Beta:
- When an incident occurs, use Tripod Beta to investigate which barriers failed and why.
- Feed findings back into the Bowtie framework to improve or redesign barriers.
For example:
- Use Bowtie to design a safety system for hazardous chemical handling.
- If a spill occurs, use Tripod Beta to investigate the failure.
- Update the Bowtie to reflect the lessons learned and strengthen the barriers.
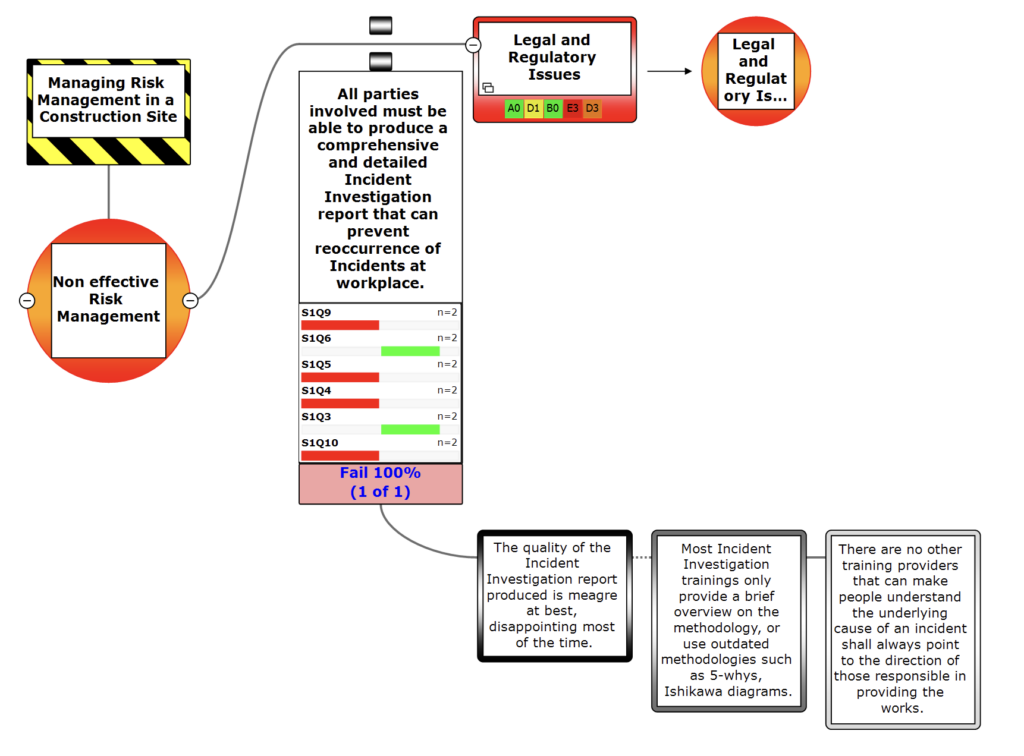
5. Key Differences at a Glance
| Aspect | Bowtie | Tripod Beta |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Proactive (before incidents) | Reactive (after incidents) |
| Focus | Hazard identification, risk assessment | Incident investigation, root cause analysis |
| Output | Risk control diagram with barriers | Root causes, failed barriers, and recommendations |
| Goal | Prevent incidents by managing risks | Prevent recurrence by fixing systemic issues |
| Primary Use Case | Planning and barrier design | Post-incident investigation |
Conclusion
While Bowtie helps prevent incidents by proactively managing risks, Tripod Beta focuses on learning from incidentsby uncovering systemic failures. Together, they create a powerful system for improving safety and operational performance through both proactive risk management and reactive learning.
